Ayurvedic Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
About Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
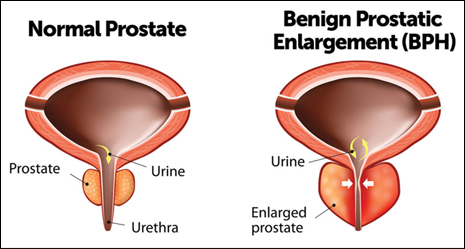
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) also known as benign prostatic hypertrophy is an enlarged prostate that can block the urethra (a tube that excretes urine out of the body.) It is very common problem after 40 years of age in men. The prostate is a small gland found only in men, located below the bladder.
Causes of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
- Changes in hormone balance and in cell growth.
- Sedentary or insufficient physical work
- Suppression of urge for urinating
- Incompatible food intake
- Lifestyle disturbance
Certain medications also trigger the symptoms:-
- Cold or sinus medications that contain decongestants or anti-histamines
- Asthma drugs (esp. inhalers)
- Allergy and hay fever drugs
Symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Nerves within the prostate and bladder may also play a role in causing the following common symptoms:
- Urinary frequency - The need to urinate frequently during the day or night (nocturia), usually voiding only small amounts of urine with each episode
- Urinary urgency - The sudden, urgent need to urinate, owing to the sensation of imminent loss of urine without control
- Hesitancy - Difficulty initiating the urinary stream; interrupted, weak stream
- Incomplete bladder emptying - The feeling of persistent residual urine, regardless of the frequency of urination
- Straining - The need strain or push to initiate and maintain urination in order to
- fully evacuate the bladder
- Disturbed sleep at night
- Decreased force of stream - The subjective loss of force of the urinary stream over time
- Dribbling - Due to a poor urinary stream
Complications of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
- In a small number of cases, BPH may cause the bladder to be blocked, making it extremely hard to urinate.
- Backed-up urine in the bladder (urinary retention), leading to bladder infections or stones, or kidney damage.
Diagnosis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
- Physical examination.
- Urine test (urinalysis)
- Digital rectal examination (DRE) to feel the size of prostate.
- Prostate specific antigen (PSA) test to rule out prostate cancer.
- Cystoscopy
Ayurvedic Approach
Ashthila along with two other conditions known as mootrakrucha and mootraaghaata caused due to aggravation of Vata especially the Apana Vayu described in ayurvedic texts coincides with the symptoms of Prostate enlargement. Mootrakruchra or difficulty in urinating is characterized by severe pain in passing urine whereas in mootraaghaata, there is total suppression or intermittent flow of urine during urination.
Herbal Remedies for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Rajamruth Vaidyashala provides best combination of effective herbal remedies such as Prostate Care Pack for ayurvedic treatment of enlarged prostate (BPH). These herbal remedies are prepared from using best quality herbs and strictly follow the principles of Ayurveda. All these herbal remedies of Rajamruth Vaidyashala are 100 percent pure, natural and vegetarian. These are free from chemicals, additives and preservatives. These are safe to use as these are free from side effects.
Dietary Recommendations
- Diet rich in whole, natural foods is excellent for the overall prostate health. Foods rich in nutrients have the potential to both help prevent and treat health issues like prostatitis, benign prostatic hypertrophy, and prostate cancer.
- Pumpkin seeds, cayenne, jackfruit seeds, broccoli, mushroom, pomegranate, Yogurt are good.
- foods, such as asparagus, bananas, and dates will delay prostate swelling
- Herbs like senna leaf to move apana vata, ajwain seed and asafetida to enhance digestion, and turmeric for inflammation.
- Avoid Pickles, squashes, some beverages like Beer, Lemonade, Cocoa, Sauces, chocolate and canned fruit juices, Citrus fruits (particularly orange juice), Watermelon, Pineapple etc.
- Avoid intake of more fluid after 7 pm to reduce the need of frequent urination.
- Take less salt as it causes fluid retention
- Dry, Cold, astringent pungent foods should be avoided.
- Food which is heavy to digest.
- Avoid Broad Beans, Tomatoes, White Corn, Yellow corn, Peas, fish and meat, Red wine, Aged wines, Coffee, Soft Drinks and Tea.

The information presented on this website is solely intended for educational purposes and should not be considered a replacement for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The statements and details on this site have not been assessed by the Food and Drug Administration. Our herbal products are entirely natural, pure, vegetarian, and efficacious. Individual results may differ, and it is advisable to consult with your healthcare professionals before using these products.
